Core Data 是 iOS SDK 中強大的數據持久化框架,允許我們存取和管理應用程式中的資料。它比直接操作 SQLite 數據庫更高效,但它的高階抽象可能讓新手感到複雜。為了讓學習更加直觀,我們將從一個簡單的範例開始,專注於 Core Data 的基本操作——插入、讀取、和刪除資料。

建立新專案,勾選 Core Data。
Core Data 預設會在 AppDelegate.swift 中加入 NSPersistentContainer 和 saveContext()。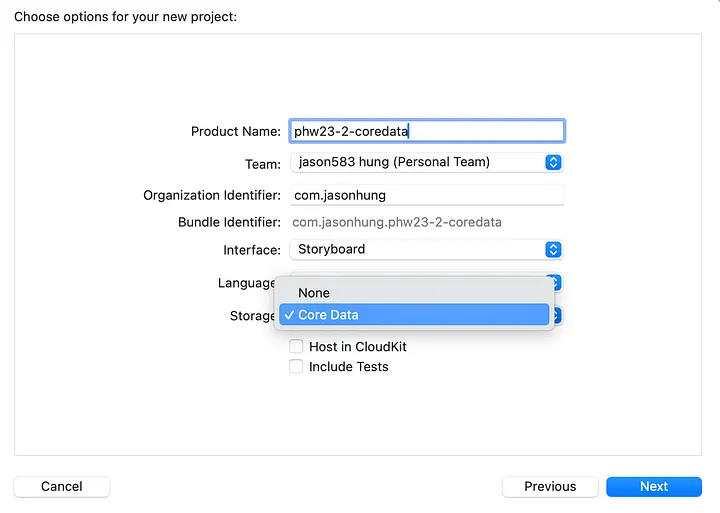
將 Core Data 的相關邏輯移至 CoreDataStack 類別中,使代碼更清晰。
import CoreData
class CoreDataStack {
static let shared = CoreDataStack()
let persistentContainer: NSPersistentContainer = {
let container = NSPersistentContainer(name: "phw23_2_coredata")
container.loadPersistentStores { storeDescription, error in
if let error = error as NSError? {
fatalError("Unresolved error \(error), \(error.userInfo)")
}
}
return container
}()
var context: NSManagedObjectContext {
return persistentContainer.viewContext
}
func saveContext () {
let context = persistentContainer.viewContext
if context.hasChanges {
do {
try context.save()
} catch {
let nserror = error as NSError
fatalError("Unresolved error \(nserror), \(nserror.userInfo)")
}
}
}
private init() {}
}
並在 SceneDelegate.swift 中修改 sceneDidEnterBackground:
func sceneDidEnterBackground(_ scene: UIScene) {
CoreDataStack.shared.saveContext()
}
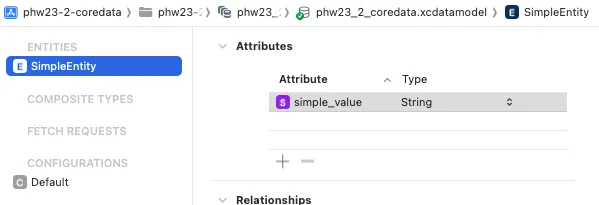
在 .xcdatamodeld 檔案中,新增一個名為 SimpleEntity 的 Entity,並添加一個屬性 simple_value(String 型別)。
在 ViewController 中,新增一個函數來儲存資料:
func insertSimpleValue(_ value: String) {
let context = CoreDataStack.shared.context
let entity = NSEntityDescription.entity(forEntityName: "SimpleEntity", in: context)!
let simpleObject = NSManagedObject(entity: entity, insertInto: context)
simpleObject.setValue(value, forKey: "simple_value")
do {
try context.save()
} catch {
print("Failed to save value: \(error)")
}
}
接著,我們撰寫一個函數來抓取資料:
func fetchSimpleValues() -> [String]? {
let context = CoreDataStack.shared.context
let fetchRequest = NSFetchRequest<NSManagedObject>(entityName: "SimpleEntity")
do {
let results = try context.fetch(fetchRequest)
return results.map { $0.value(forKey: "simple_value") as? String }.compactMap { $0 }
} catch {
print("Failed to fetch values: \(error)")
return nil
}
}
在 viewDidLoad() 中呼叫這些方法,並更新顯示資料:
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
insertSimpleValue("Jason:\(Int.random(in: 0..<100))")
updateStringLabel()
}
func updateStringLabel() {
if let values = fetchSimpleValues() {
stringLabel.text = values.joined(separator: "\n")
}
}

那我們再添加兩個按鈕,一個用於新增資料,一個用於刪除所有資料。
新增一個刪除所有資料的函數:
func deleteAllData() {
let context = CoreDataStack.shared.context
let fetchRequest = NSFetchRequest<NSFetchRequestResult>(entityName: "SimpleEntity")
let batchDeleteRequest = NSBatchDeleteRequest(fetchRequest: fetchRequest)
do {
try context.execute(batchDeleteRequest)
try context.save()
} catch {
print("Failed to delete all data: \(error)")
}
}
並為按鈕添加相應的動作:
@IBAction func AddString(_ sender: Any) {
insertSimpleValue("Jason:\(Int.random(in: 0..<100))")
updateStringLabel()
}
@IBAction func deleteAll(_ sender: Any) {
deleteAllData()
updateStringLabel()
}
透過本篇簡單的 Core Data 操作範例,我們成功學習了如何在 iOS 應用中執行插入、查詢、刪除資料等基本操作。這些基礎操作為我們理解 Core Data 的運作流程提供了寶貴的實踐經驗,讓開發者在無需深入接觸底層資料庫操作的情況下,便可實現資料持久化。Core Data 的優勢在於其高階抽象層,讓開發者能夠專注於業務邏輯,而不用直接處理 SQL 查詢或資料庫管理。
雖然本篇範例只處理了單一欄位的基本操作,但這已經為後續更進階的應用打下了基礎。在實際開發中,Core Data 能夠處理更複雜的資料結構,包括關聯表、多重條件查詢,以及離線模式等高級功能。透過掌握這些功能,開發者可以更靈活地設計資料模型,為應用提供高效的資料儲存與管理解決方案。
明天我們進一步剖析 Core Data 與 SQLite 之間的關聯,讓你更深入理解其背後的資料庫結構。希望本篇範例能幫助你順利打開 Core Data 的大門,並為你的 iOS 開發旅程帶來更多可能性!
